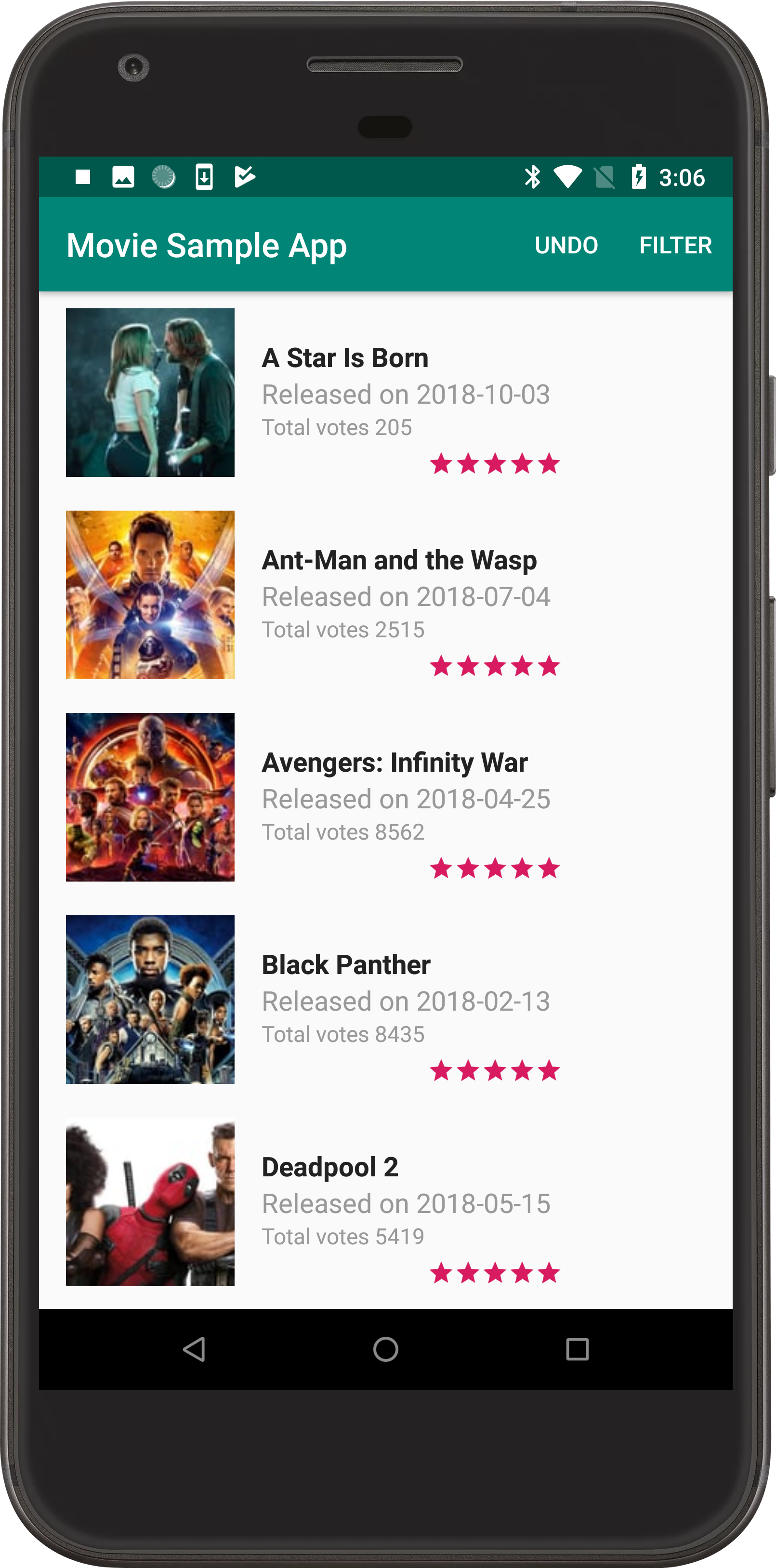
It is an sample android movie application that builds with a lot of new tools like MVVM Software Architecture Pattern, A lot of things from Android Jetpack, and using very cool libraries like RxJava, Dagger2, Retrofit and more with the flavour of S.O.L.I.D Principles and Clean Code Architectur.
Github Project
You can check the whole project here.
Gitflow Workflow
Working with teams can be quite challenging if there is no process in place to review and check code before it is merged, or more importantly to prevent ominous code from getting to production.
One important tool that can make collaboration with other developers hassle free, is a version control system. The most popular system is Git.
Git is a system used for tracking changes in files and coordinating work on those files among multiple people; it is primarily used for source code management in development. It is free, open source and it handles everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
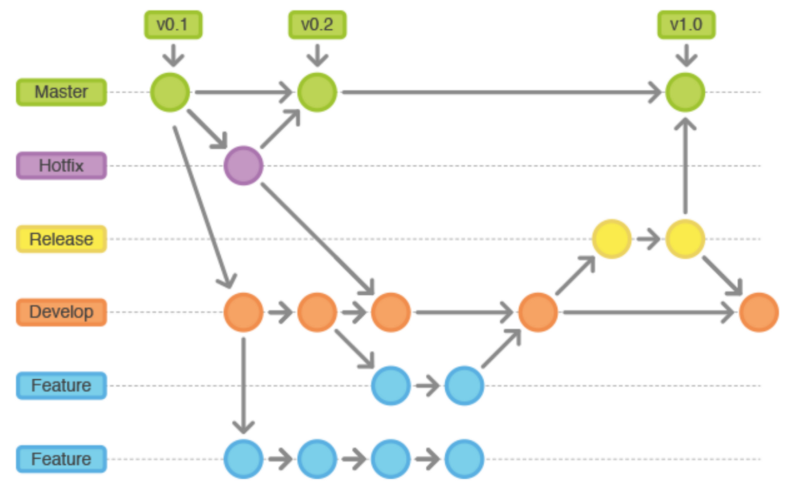
So the idea is to have two major branches named Master and Dev which are linked to two environments: Staging (https://staging.exampleapi.com) and Production (https://exampleapi.com). Typically you should have your staging be an exact replica of your production environment.
Types of Branches :
- Master Branch is the production-ready version of our codebase which is automatically deployed to our production environment (https://exampleapi.com), with everything fully tested and checked. “Thou shall not touch this branch.”
- Dev Branch is where all feature branches are merged after pull requests have been thoroughly checked, fixed, and all tests are performed. Once all builds pass, this branch is deployed to the staging environment (https://staging.exampleapi.com) for QA and UATs.
- Release Branch should be created from the Dev branch for final audit eg: cleanup and remove comments, versioning etc. This branch is tagged, and then merged to both Master and Dev branches.
Tools and Technologies Used
- Using Some Cool Tools from Android Architecture Components and Android Jetpack :
- ViewModel is a class that is responsible for preparing and managing the data for an Activity or a Fragment. It also handles the communication of the Activity / Fragment with the rest of the application (e.g. calling the business logic classes).
- LiveData is a data holder class that can be observed within a given lifecycle. This means that an Observer can be added in a pair with a LifecycleOwner, and this observer will be notified about modifications of the wrapped data only if the paired LifecycleOwner is in active state.
- LifecycleOwner is a class that has an Android lifecycle. These events can be used by custom components to handle lifecycle changes without implementing any code inside the Activity or the Fragment.
- Room is a Database Object Mapping library that makes it easy to access database on Android applications. Rather than hiding the detail of SQLite, Room tries to embrace them by providing convenient APIs to query the database and also verify such queries at compile time. This allows you to access the full power of SQLite while having the type safety provided by Java SQL query builders.
- Using Another Some Cool Tools and Libraries :
- RxJava is Java implementation of Reactive Extension (from Netflix). Basically it’s a library that composes asynchronous events by following Observer Pattern. You can create asynchronous data stream on any thread, transform the data and consumed it by an Observer on any thread. The library offers wide range of amazing operators like map, combine, merge, filter and lot more that can be applied onto data stream.
- Dagger is a fully static, compile-time dependency injection framework for both Java and Android. It is an adaptation of an earlier version created by Square and now maintained by Google.
- Retrofit is a REST Client for Android and Java by Square. It makes it relatively easy to retrieve and upload JSON (or other structured data) via a REST based web service. In Retrofit you configure which converter is used for the data serialization. Typically for JSON you use GSON, but you can add custom converters to process XML or other protocols. Retrofit uses the OkHttp library for HTTP requests.
- Gson is a Java library that can be used to convert Java Objects into their JSON representation. It can also be used to convert a JSON string to an equivalent Java object. Gson can work with arbitrary Java objects including pre-existing objects that you do not have source-code of.
- LeakCanary identifies an object that is longer needed and finds the chain of references that prevents it from being garbage collected. A memory leak is a programming error that causes your application to keep a reference to an object that is no longer needed. As a result, the memory allocated for that object cannot be reclaimed, eventually leading to an OutOfMemoryError crash.
- Timber is an API for Android’s Log class. It basically enhances the logs from Android. We do that by plating a Tree, and each time we log something, the behaviour may change depending on which Tree implementation end up been called. But here we used Timberkt since this library builds on Timber with an API that’s easier to use from Kotlin. Instead of using formatting parameters, you pass a lambda that is only evaluated if the message is logged.
- Glide is a fast and efficient open source media management and image loading framework for Android that wraps media decoding, memory and disk caching, and resource pooling into a simple and easy to use interface.
Clean Architecture
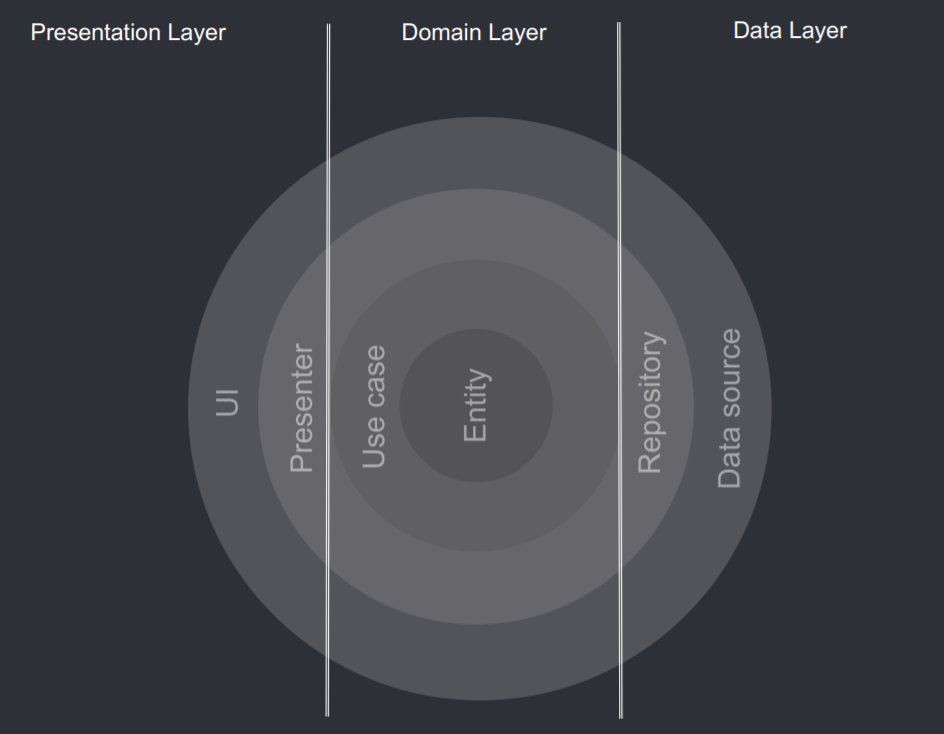
Trying to follow and implement as much as I can The Clean Code Architecture :
- Presentation Layer contains UI (Activities & Fragments) that are coordinated by Presenters/ViewModels which execute 1 or multiple Use cases. Presentation Layer depends on Domain Layer.
- Domain Layer is the most INNER part of the onion (no dependencies with other layers) and it contains Entities, Use cases & Repository Interfaces. Use case combines data from 1 or multiple Repository Interfaces.
- Data Layer contains Repository Implementations and 1 or multiple Data Sources. Repositories are responsible to coordinate data from the different Data Sources. Data Layer depends on Domain Layer.
The Guide to App Architecture proposes an architecture with the following main components:
- A local database that serves as a single source of truth for data presented to the user and the actions the user has taken to change that data.
- A web API service.
- A repository that works with the database and the API service, providing a unified data interface
- A ViewModel that provides data specific for the UI
- The UI, which shows a visual representation of the data in the ViewModel
So, our app follows the architecture recommended in the Guide to App Architecture, using Room as local data storage. Here’s what you will find in each package:
- api - contains Github API calls, using Retrofit
- db - database cache for network data
- data - contains the repository class, responsible for triggering API requests and saving the response in the database
- ui - contains classes related to displaying an
Activitywith aRecyclerView - model - contains the
Repodata model, which is also a table in the Room database; andRepoSearchResult, a class that is used by the UI to observe both search results data and network errors
Architecture Used
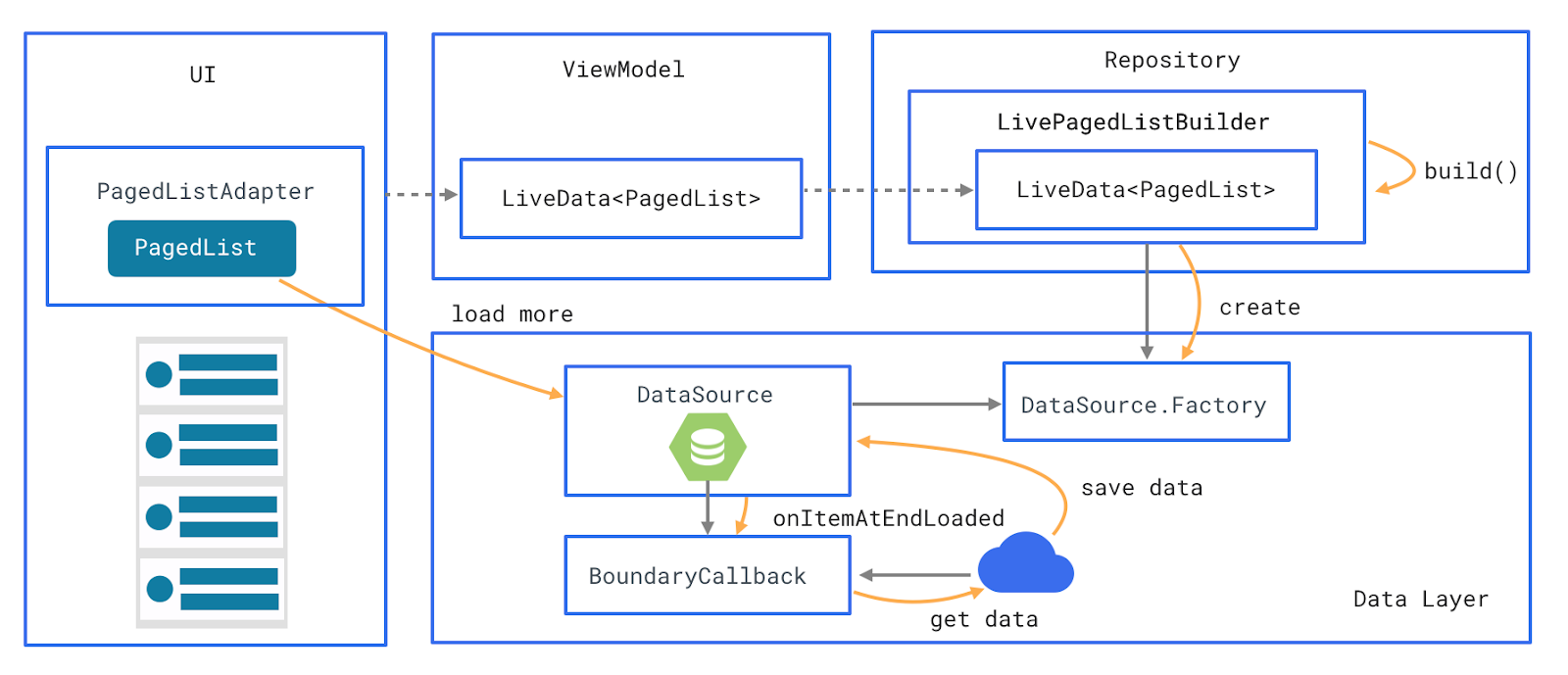
The following diagram shows all the modules in our recommended architecture and how they interact with one another:
The main players in the MVVM pattern are:
- The View that informs the ViewModel about the user’s actions. It is the actual user interface in the app. It can be an
Activity, aFragmentor any custom AndroidView. - The ViewModel exposes streams of data relevant to the View. It is a model for the View of the app: an abstraction of the View. The ViewModel retrieves the necessary data from the DataModel, applies the UI logic and then exposes relevant data for the View to consume.
- The DataModel abstracts the data source. The ViewModel works with the DataModel to get and save the data. It exposes data easily consumable through event streams like RxJava’s Observables or LiveData as we used here in our app. It composes data from multiple sources, like the network layer, database or shared preferences and exposes easily consumable data to whomever needs it. The DataModels hold the entire business logic.
TO DO
CI and CD
Before started explaining What is what? Let’s introduce todays era buzz word DevOps. What is DevOps? This term are not specific to android only. They are generic we can use them with any of the technology.
Working on the big organisation and enterprise app development. Working with large teams in agile process it could be very hard to track the development progress, code integration, code review and deployment process. Always learn from the past experience thats the best way to gain the experience and improve your self.
CI is Continuous Integration, a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early. CD is Continuous Deployment or Delivery. By integrating regularly, you can detect errors quickly, and locate them more easily.
Pros of CI and CD :
- CI reducing the risk and overheads.
- Defects are detected and fixed sooner.
- Analysing and Reporting.
- Automated Testing, you can do pre commit and post commit testing, pre deploy, post deploy testing.
- Code control and code versioning.
- Prevent wrong commits, missing file and resource while committing code.
- It will reduce efforts, time and money.
- Build automation.
- Deployment Automation.
So, I am going to use CircleCi for Continues Integration and Fastlane for Continues Deployment and Delivery.
Unit Testing and UI Testing
Usually I am using JUnit, Mockito with Dagger Dependency Injection for writing my unit tests but recently I tried Spek which from my point of view a very helpful tool since it makes you able to write both TDD and BDD according to your use and test case.
Static Code Analysis
The static code analysis tools are widely used in Java development to improve the codebase and identify potential vulnerabilities along with design flaws. Every tool has its own feature, purpose and strength which helps in increasing the code quality and makes you a better developer.
I am going to use FindBugs and Detekt for static code analysis.